Description
Data and Figures
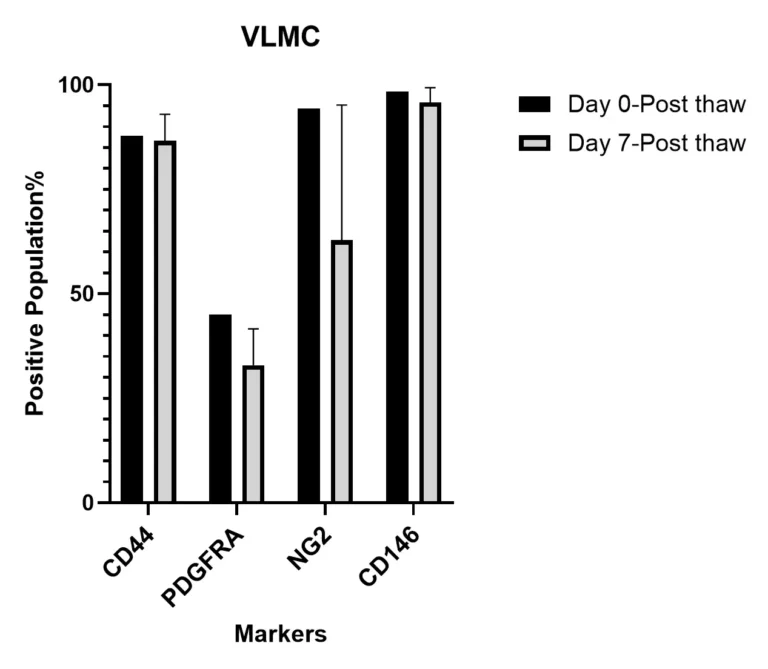
Cellular Characterization by Flow Cytometry
Flow cytometry data shows homogeneity of TrailBio® Vascular Leptomeningeal Cells upon thawing (day 0) and post-thaw (day 7). More than 80% of cells express CD44/CD146/NG2, and 30% of cells express PDGFRA, confirming the cellular identity of neuroectoderm-derived VLMCs.
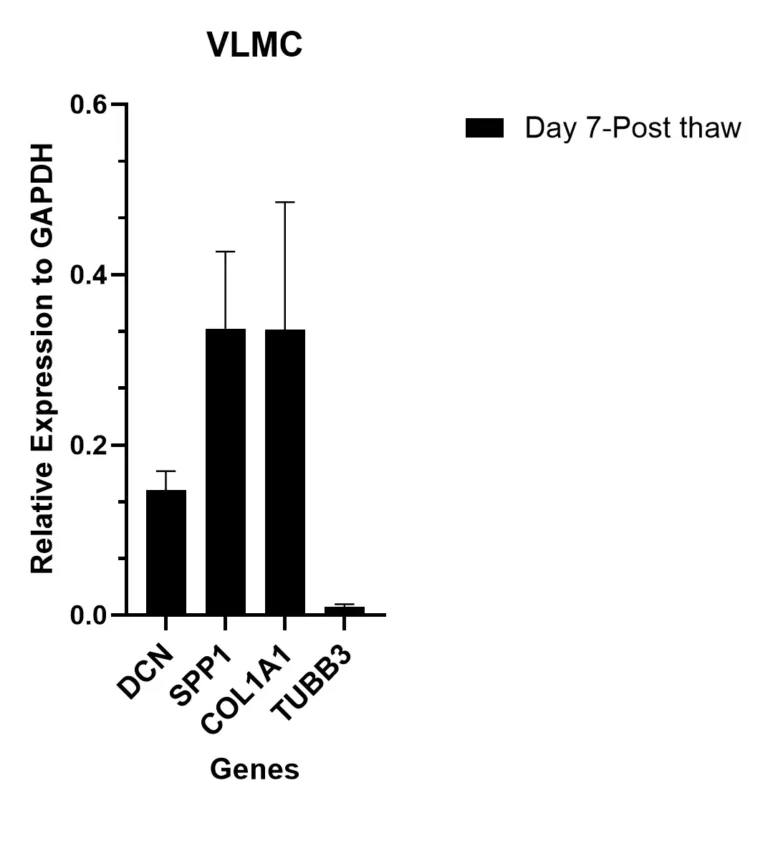
Gene Expression Analysis by qRT-PCR
qRT-PCR data shows high expression of selected VLMC genes, including DCN, SPP1 and COL1A1 relative to control gene GAPDH on day 7 post-thaw. In contrast, neuronal control gene TUBB3 is shows low expression in day 7 post-thaw cultures.
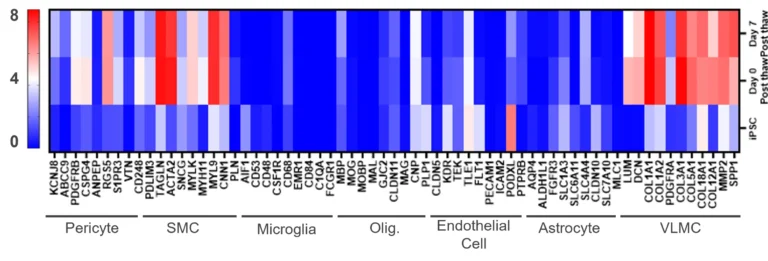
Gene Expression Analysis by RNA-seq
Bulk RNA-seq analysis of TrailBio® Vascular Leptomeningeal Cells shows distinct gene expression signatures of VLMCs compared to iPSCs and selected relevant cell types upon thawing (day 0) and post-thaw culture (day 7).
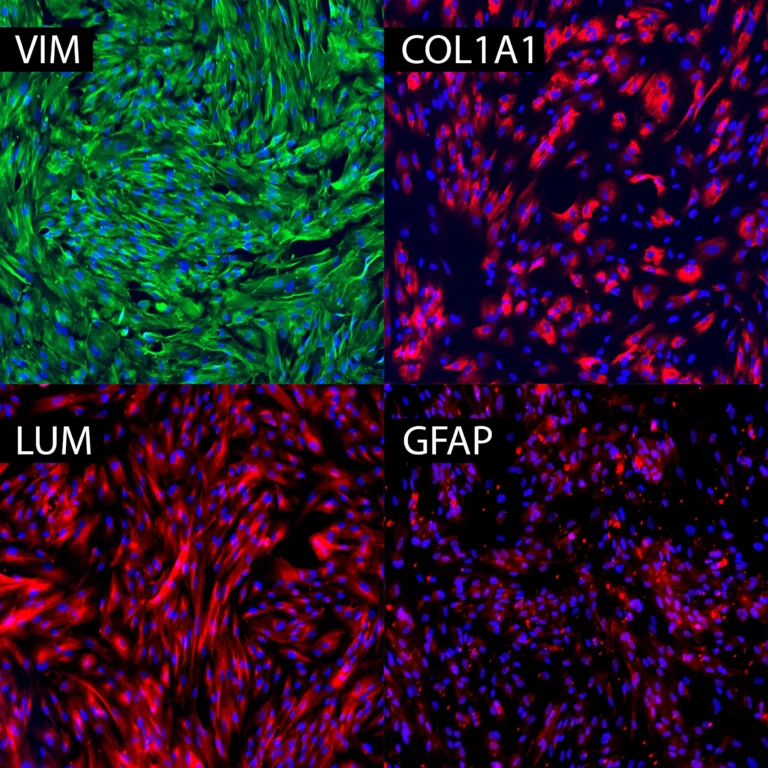
Expression of VLMC Markers by Immunocytochemistry
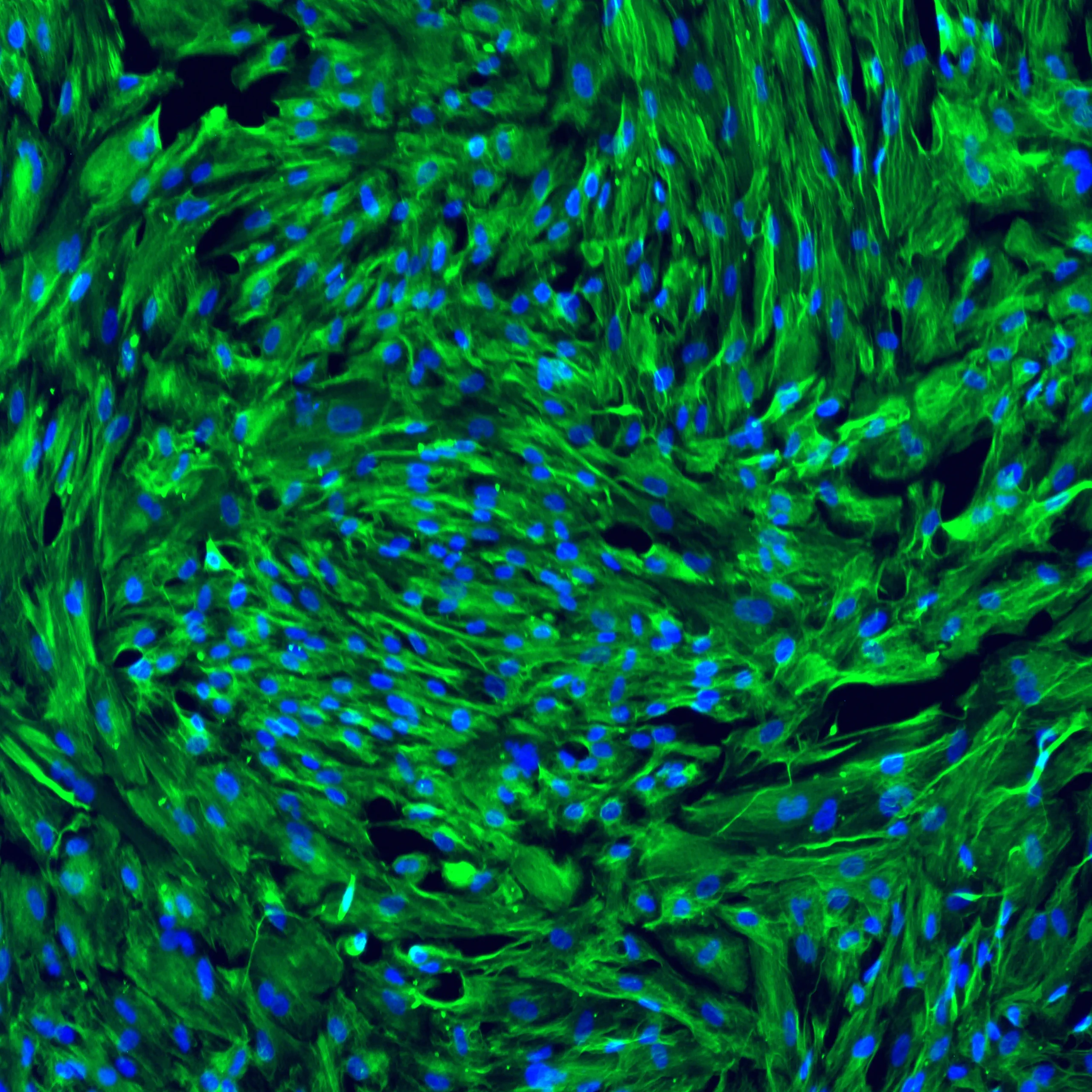
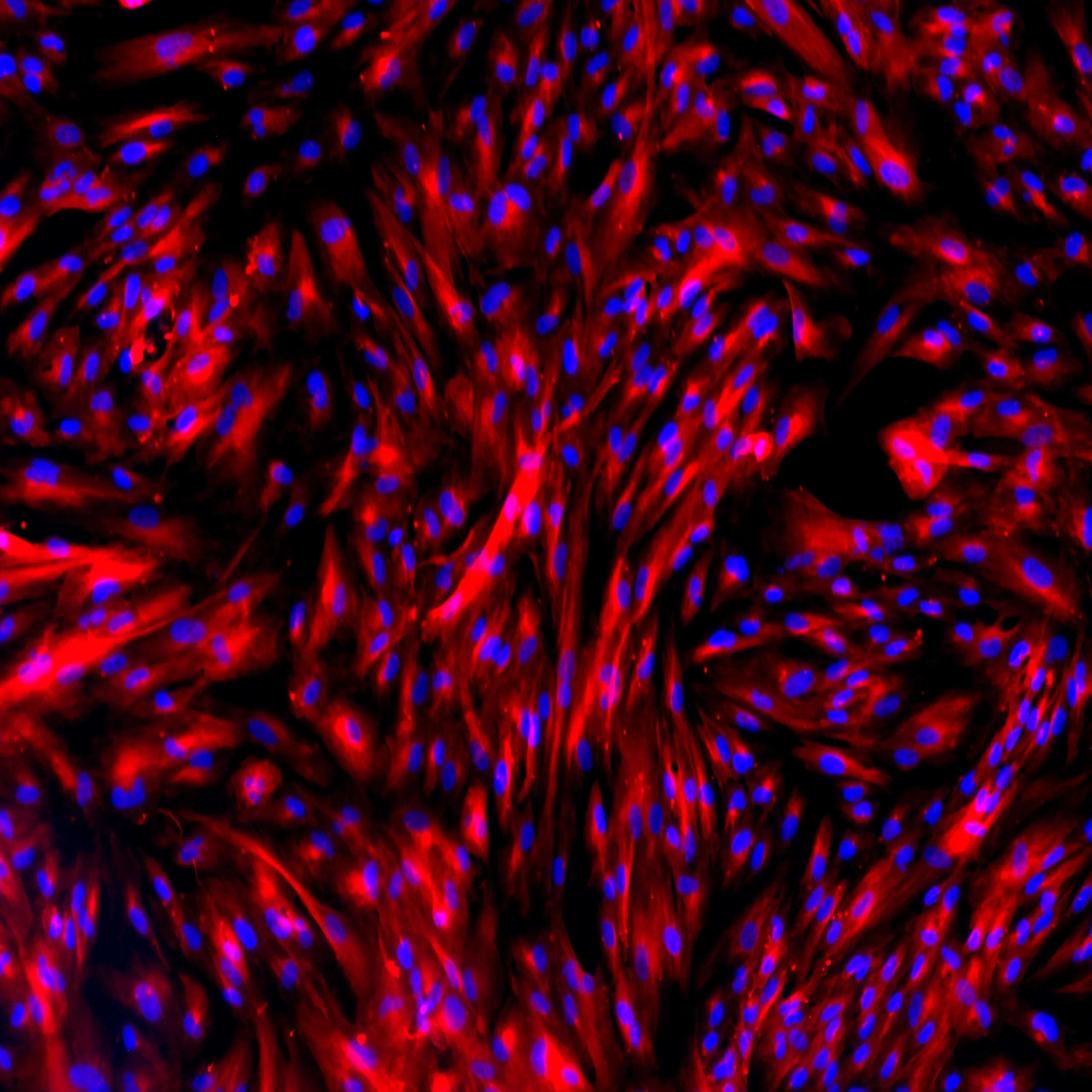
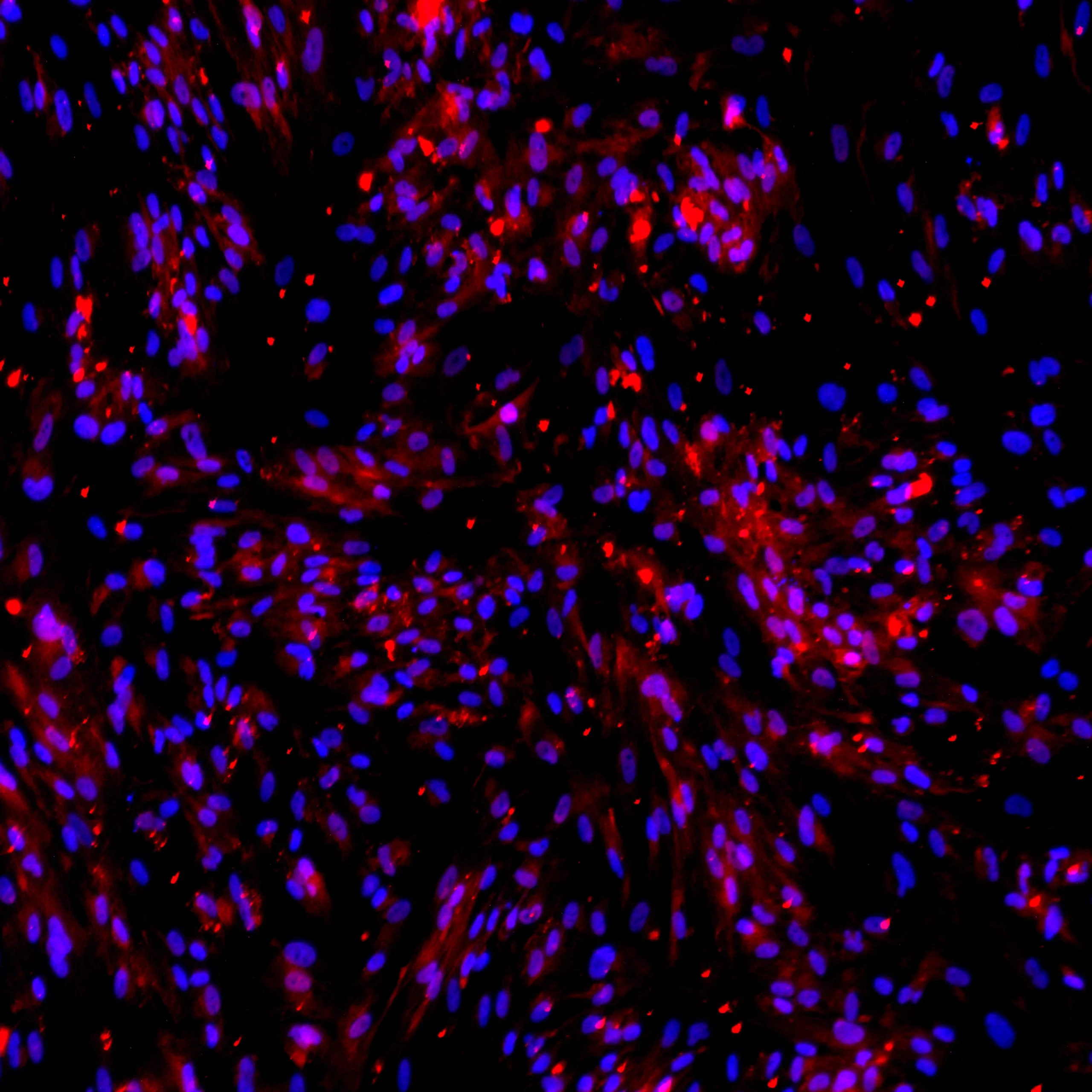
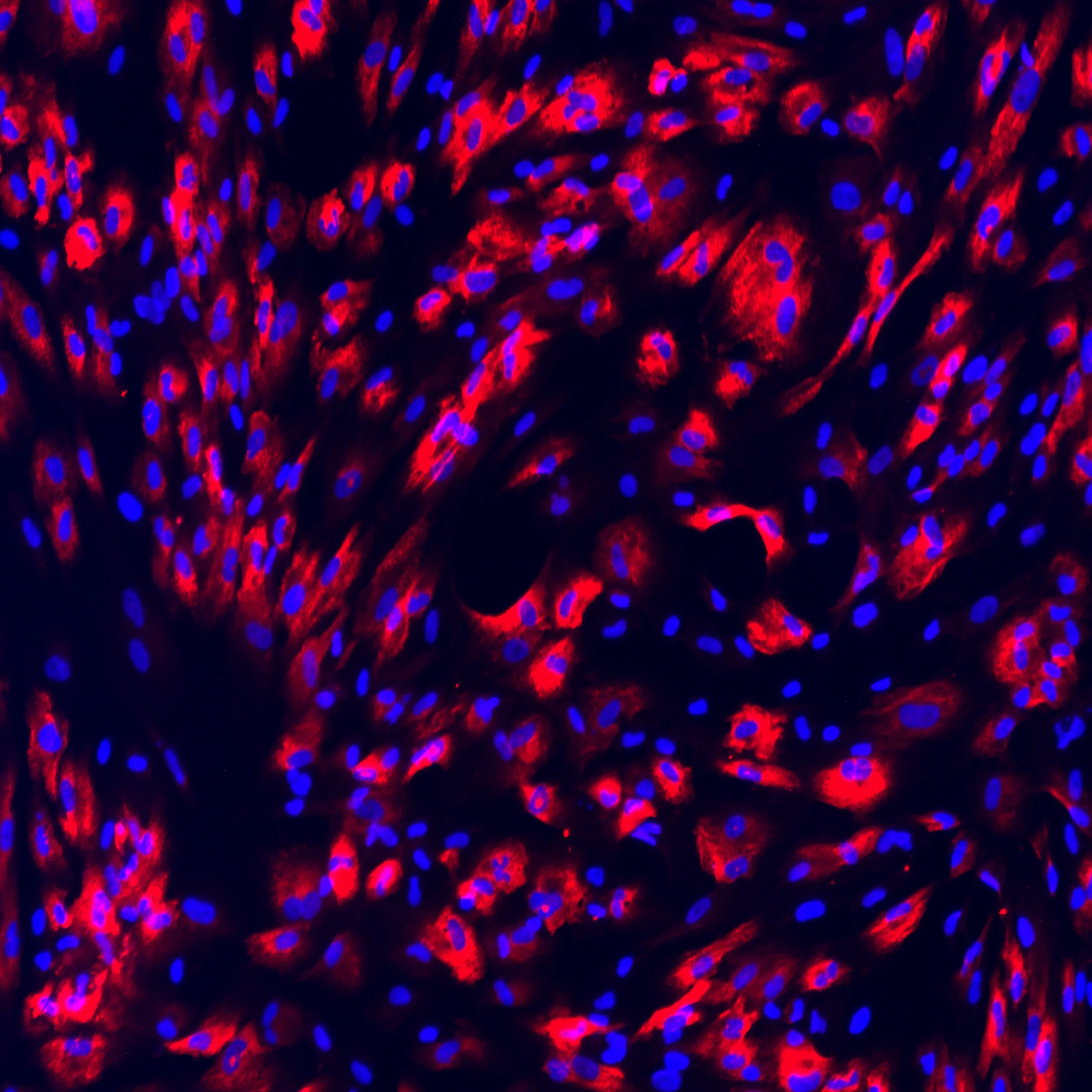
Protein expression of selected VLMC markers in TrailBio® Vascular Leptomeningeal Cells were validated by immunocytochemistry in post-thaw cultures (day 7). ECM proteins lumican (LUM) and collagen-1a (Col1A1) and structural protein vimentin (VIM) (expressed in endothelial cells and glial cells) were detected in the majority of cells. Absence of the astrocytic marker glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) confirmed that, despite the presence of common markers between VLMCs and astrocytes, cells do not differentiate into astrocytes in culture. Nuclei stained with DAPI. Imaging performed at 20X magnification.
Technical Info and Resources
Frequently Asked Questions
What are iPSC-derived Vascular Leptomeningeal cells (VLMCs)?
Induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived vascular leptomeningeal cells (VLMCs) are specialized fibroblast-like cells found in the meninges. They play a key role in blood-brain barrier function, immune surveillance and neurovascular interactions.
How do VLMCs function within the blood-brain barrier (BBB)?
Vascular Leptomeningeal cells interact with other cell types, such as endothelial cells, astrocytes and pericytes, to form a tightly regulated barrier. VLMCs help maintain the blood-brain barrier’s selective permeability, ensuring that essential nutrients can pass through while harmful substances are kept out.
How are VLMCs different from pericytes?
VLMCs are derived from the neuroectoderm, while pericytes come from the mesoderm. Functionally, VLMCs contribute to the extracellular matrix and immune regulation in the meninges, whereas pericytes support vascular stability, blood-brain barrier maintenance and capillary constriction.
What applications are TrailBio® Vascular Leptomeningeal Cells suitable for?
VLMCs function as part of the blood-brain barrier and also play a critical role in neural inflammation and the maturation of pericyte progenitors in blood-brain barrier.
Areas of potential study include:
- Leptomeningeal Disease
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Traumatic Brain Injury
What markers do Trailhead VLMCs express?
TrailBio iPSC-derived VLMCs are characterized by the expression of key leptomeningeal markers, including DCN, LUM, COL1A1, PDGFRA, CD44 and CD146.