Description
Data and Figures
Phenotypic & Transcriptomic Characterization
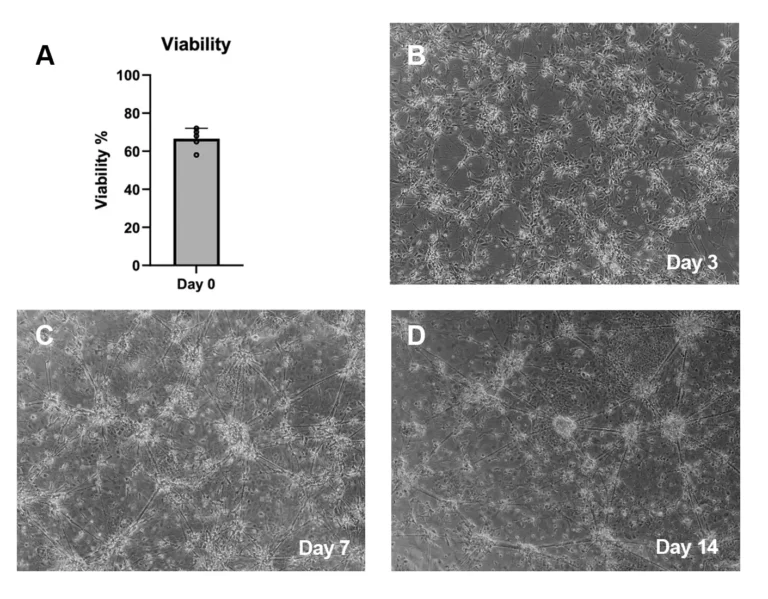
Cell Viability and Morphology
TrailBio® A9 Dopaminergic Neuron progenitors exhibit high viability upon thaw (A) and display characteristic morphological features of maturing dopaminergic neurons as shown in brightfield images at day 3 (B), day 7 (C) and day 14 (D) post–thaw.
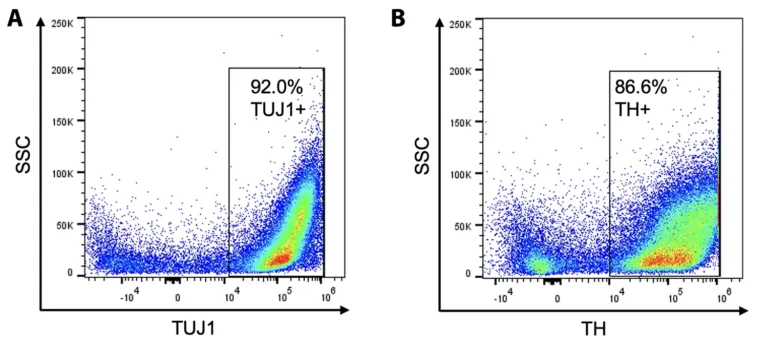
Cellular Characterization by Flow Cytometry
Day 14 post-thaw matured TrailBio® A9 Dopaminergic Neurons exhibit strong expression of canonical neuronal markers, (A) TUBB 3 (Beta-Tubulin III as shown using the antibody TUJ1) and (B) TH (Tyrosine Hydroxylase) as shown by FACS.
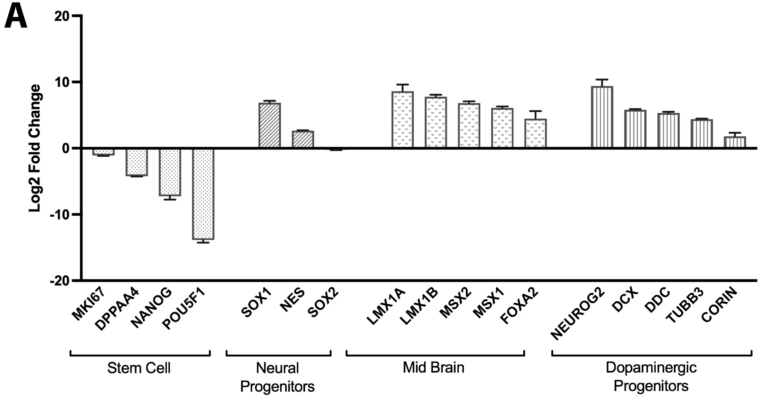
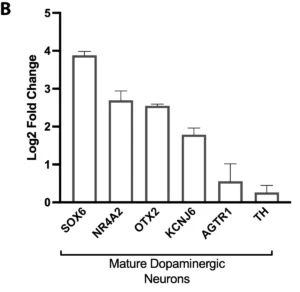
Gene Expression Analysis by RNA-Seq
Bulk RNA-sequencing confirms the successful stepwise differentiation of TrailBio® A9 cells into dopaminergic neurons. Gene expression analysis was performed at key developmental stages. (A) Comparison of dopaminergic progenitors to the initial iPSC population reveals a significant downregulation of pluripotency markers (e.g., POU5F1, NANOG) and a robust upregulation of genes associated with neural fate (PAX6), midbrain identity (FOXA2, LMX1A) and dopaminergic specification (NR4A2). This confirms a successful exit from pluripotency and appropriate regional patterning. (B) Subsequent comparison of day 14 neurons to the progenitor population demonstrates a marked induction of genes critical for dopaminergic neuron function and maturation, including dopamine synthesis (TH), transport (SLC6A3/DAT) and synaptic transmission (SYP), indicating the generation of mature post-mitotic neurons.
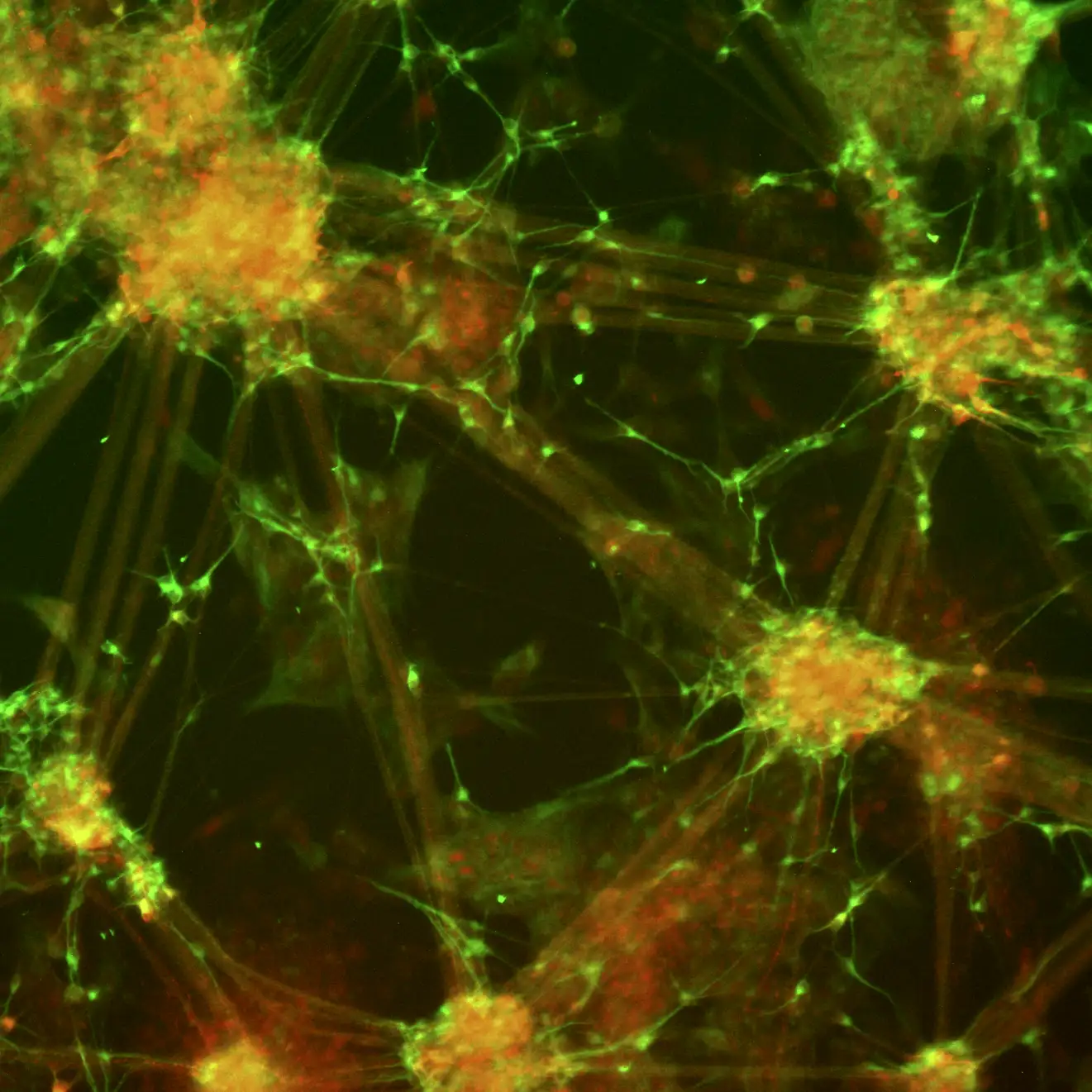
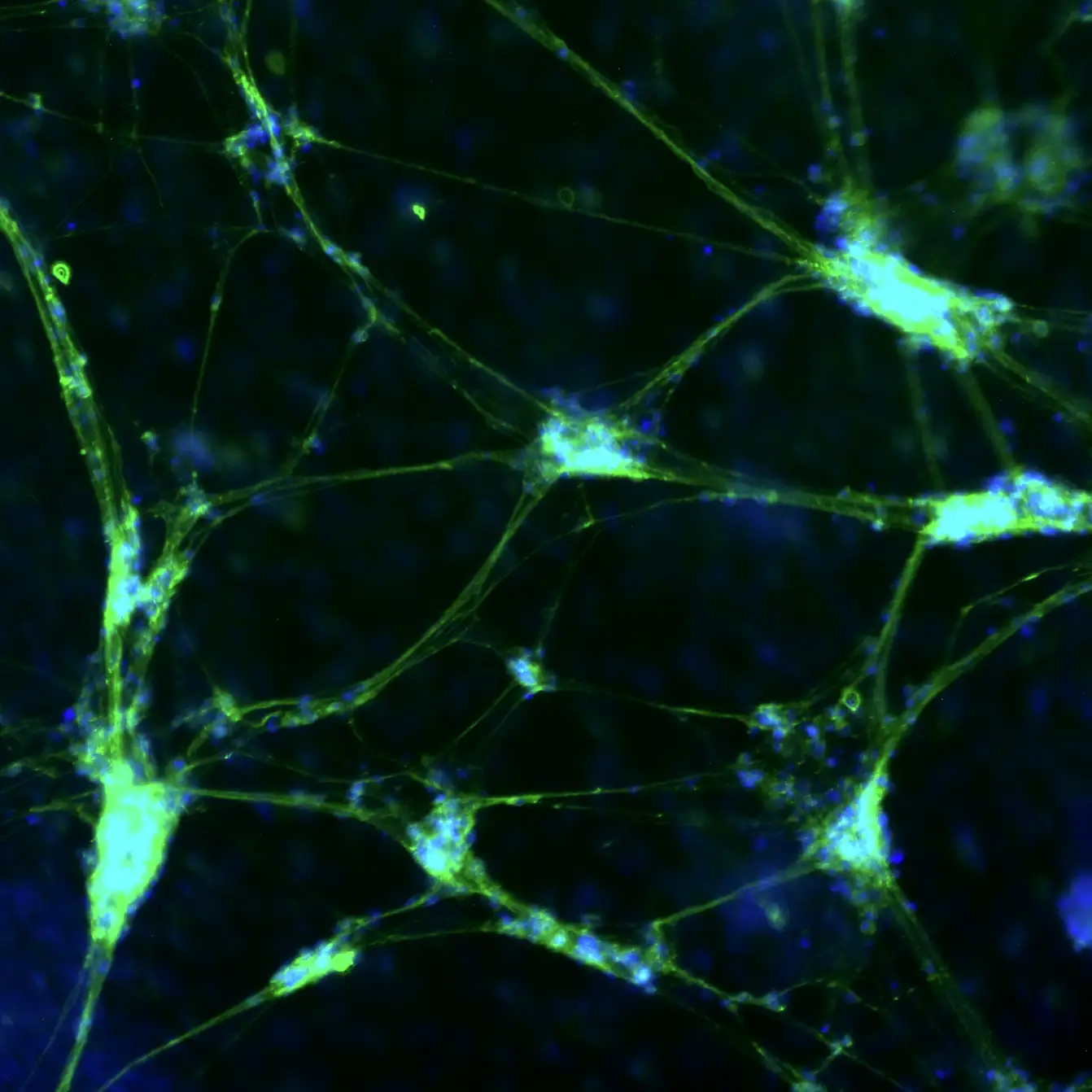
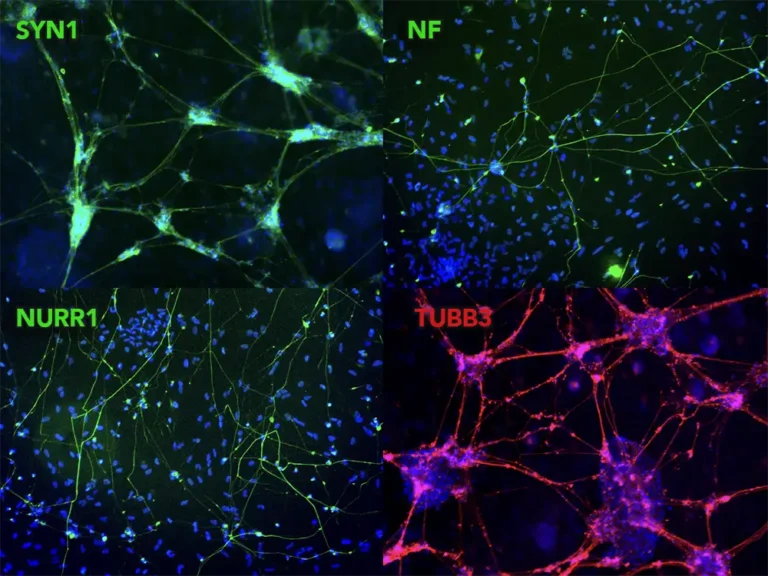
Expression of Neuronal Markers by Immunocytochemistry
TrailBio® A9 Dopaminergic Neurons express typical markers of neural differentiation. Immunocytochemistry of day 14 post-thaw cells show expression of Synapsin 1 (SYN1), Neurofilament (NF), Nuclear receptor-related factor 1 (NURR1), Beta-Tubulin III (TUBB3) and nuclei (DAPI). Images were taken at 10X magnification on the EVOS M7000 Imaging System.
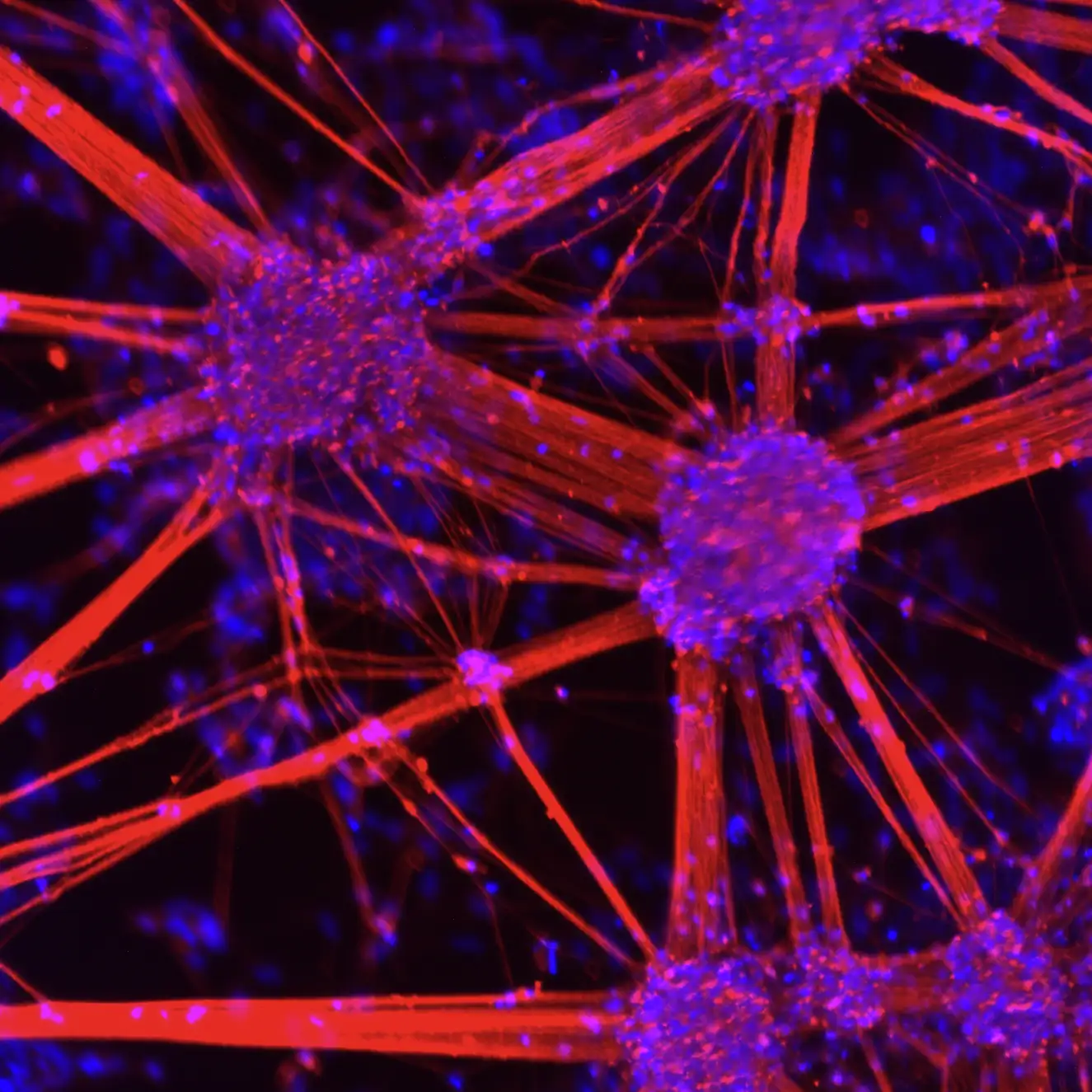
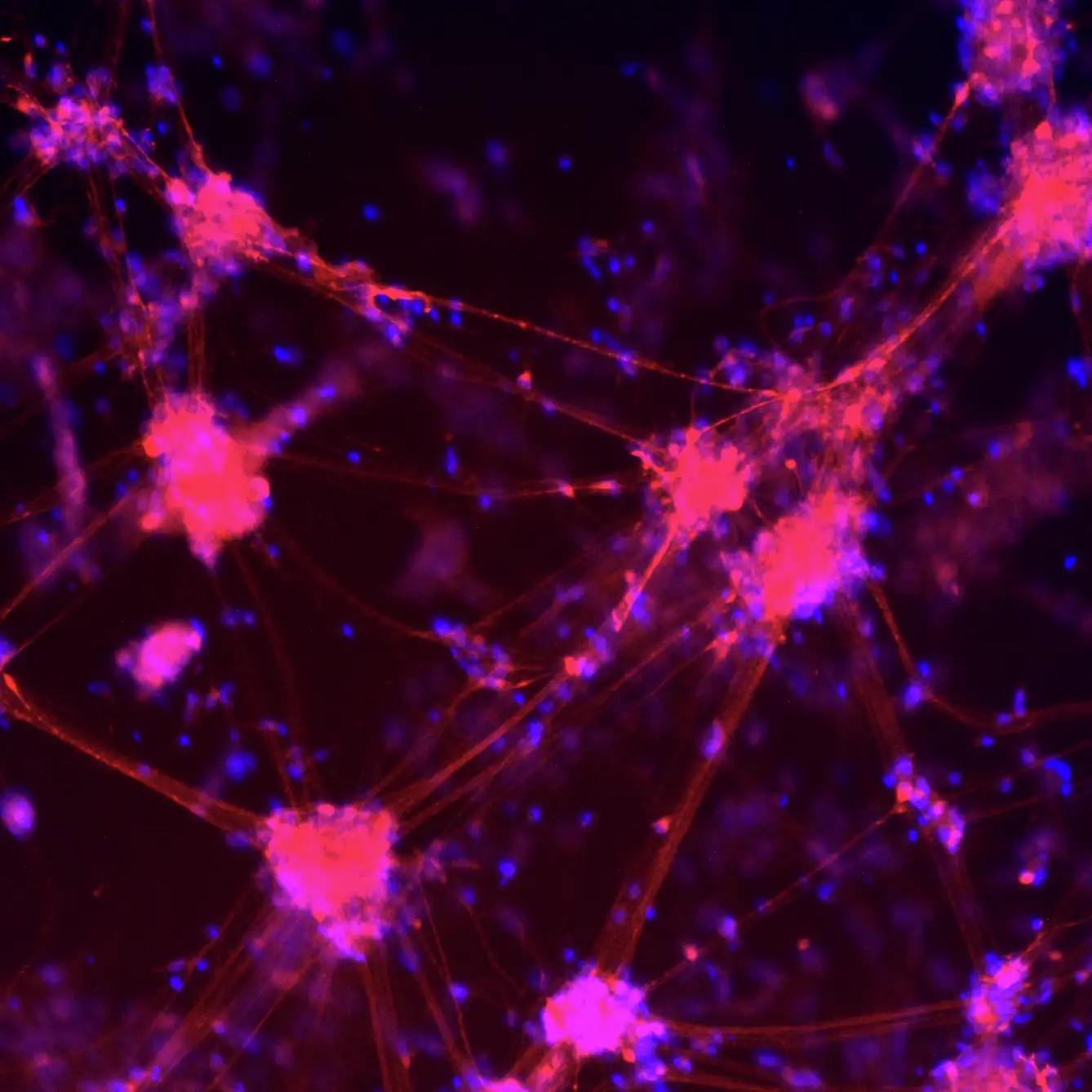
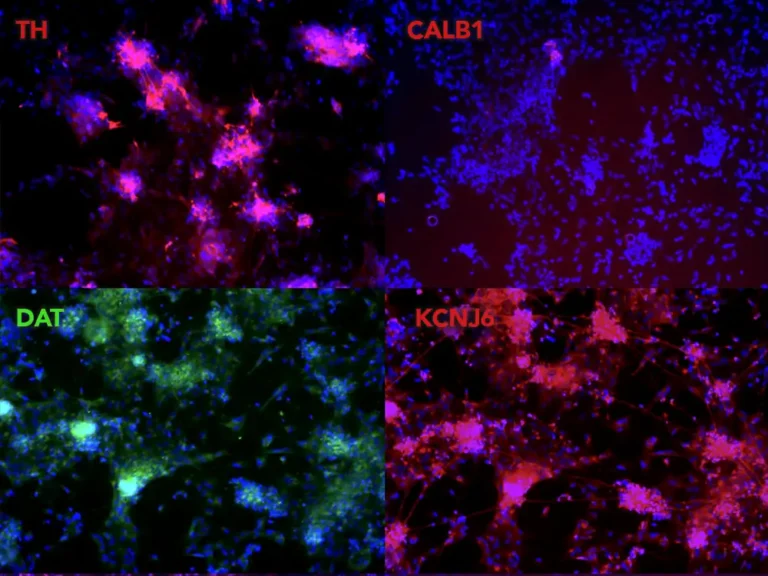
Expression of A9-Specific Markers by Immunocytochemistry
TrailBio® A9 Dopaminergic Neurons display a specific A9 marker profile. Immunocytochemistry of day 14 post-thaw neurons shows expression of Tyrosine Hydroxylase (TH), cells lacking expression of CALB1 (an A10 subtype marker), Dopamine Transporter (DAT) and the A9-specific potassium channel KCNJ6. Nuclei are stained with DAPI. Images were taken at 10X magnification on the EVOS M7000 Imaging System.
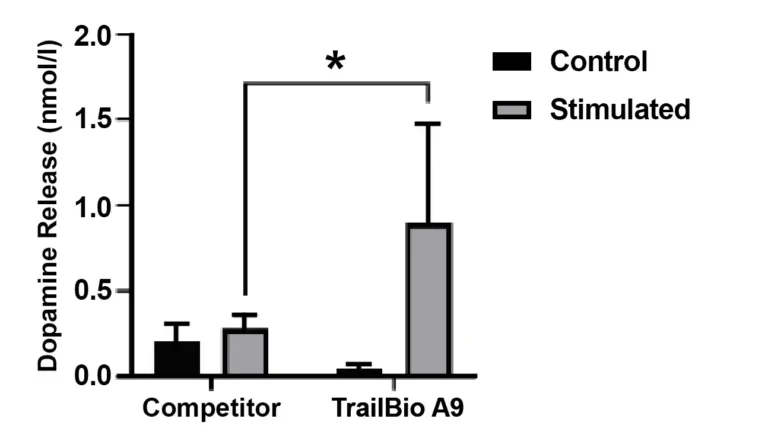
Functional Release of Dopamine by ELISA
Functional characterization and comparison of TrailBio® A9 Dopaminergic Neurons with commercially available competitor iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons. Cultured cells were stimulated with 50 mM KCl for 15 minutes at 37 °C to assess dopamine release into the medium using ELISA. Controls were medium from unstimulated cells. Dopamine release from TrailBio® A9 Dopaminergic Neurons are significantly higher than competitor cells.
Technical Info and Resources
Frequently Asked Questions
What are A9 dopaminergic neurons?
A9 dopaminergic neurons are a distinct subtype of midbrain neurons located in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc), where they play a key role in motor control. They are characterized by expression of the transcription factor SOX6, which distinguishes them from other dopaminergic subtypes such as A10 neurons, which are primarily involved in reward and motivation pathways. A9 neurons are particularly vulnerable in Parkinson’s disease, making access to high-quality iPSC-derived A9 dopaminergic neurons valuable for disease modeling and evaluating cell-based therapeutic strategies both in vitro and in vivo.
What applications are TrailBio® A9 Dopaminergic Neurons suitable for?
TrailBio® A9 Dopaminergic Neurons can be used in a range of applications, including modeling neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, investigating dopamine dysregulation, conducting neurotoxicity assays, advancing organ-on-a-chip systems and supporting drug discovery efforts. Their selective vulnerability in Parkinson’s disease makes them especially valuable for disease modeling and therapeutic development.
What markers do these A9 cells express?
The TrailBio® A9 Dopaminergic Neurons express Tyrosine Hydroxylase, SLC6A3 (DAT), KCNJ6, NR4A2 (NURR1) and transcription factor SOX6 along with pan neuronal mature markers such as MAP2 and SYN1. They do not express CALB1, a typical A10 marker.
What value do iPSC-derived A9 dopaminergic neurons offer?
A9 dopaminergic neurons play a critical role in movement regulation and are disproportionately affected in Parkinson’s disease. TrailBio® A9 Dopaminergic Neurons enable scientists to have a human-specific platform to investigate disease mechanisms, develop therapies and accelerate drug discovery.